Cannabis and Your Brain: Shocking New Discoveries
Cannabis has always been a topic that sparks heated debate. Recent research is uncovering new details about how it affects our brains. These studies show both promise and potential danger. As scientists learn more, we are beginning to understand how cannabis influences mood, thinking, and even medical treatment options. In this article, we explore new discoveries, from how cannabis interacts with brain chemicals to the subtle differences between key compounds like THC and CBD.
Cannabis and Neurotransmitters
How Cannabis Interacts With Brain Chemistry
Our brains rely on chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters, to send signals between cells. Cannabis contains active compounds that tap into this system. These substances link with special receptors, known as CB1 and CB2, found throughout the brain and body. By affecting these receptors, cannabis can change the flow of chemical signals.
The Endocannabinoid System
Scientists call the network of receptors, messengers, and enzymes that interact with cannabis the “endocannabinoid system.” This system helps regulate mood, appetite, memory, and even pain. When cannabis chemicals enter the system, they can alter these processes in unpredictable ways. This might explain why cannabis can make some people feel relaxed, but others feel anxious or paranoid.
Dopamine and Other Neurotransmitters
Cannabis can influence levels of dopamine, a key chemical involved in motivation and pleasure. Some studies show that cannabis use may flood the brain with extra dopamine at first. Over time, this can change how the brain responds to rewards. Other neurotransmitters, like GABA and glutamate, also come into play. Shifts in their balance may affect mood, learning, and overall cognitive performance.
Long-Term Changes
Repeated cannabis exposure may rewire parts of the brain. Young people who use cannabis heavily might face altered development of certain brain regions. These changes could affect memory, focus, and emotional regulation. While more research is needed, the message is clear: cannabis interacts deeply with our brain chemistry.
THC vs. CBD: Diverse Effects
Two Major Compounds
Cannabis contains many active chemicals, but two stand out: THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). THC produces the “high” linked with cannabis use. CBD does not cause a high, and may even counter some of THC’s more troubling effects.
Psychoactive vs Non-Psychoactive
THC binds strongly to CB1 receptors, which are abundant in brain regions controlling thinking and emotions. This causes the classic psychoactive effects: euphoria, altered time perception, and sometimes anxiety or paranoia. In contrast, CBD has a weaker effect on these receptors. It may help calm the mind without causing intense highs.
Therapeutic Potential
Some people find that CBD reduces pain, eases anxiety, and soothes inflammation. These potential benefits have led to an explosion of CBD products on the market. Yet, not all claims are backed by solid science. While THC can be helpful for certain conditions, its psychoactive side effects limit its medical use.
Ratios and Strains
Different cannabis strains contain varying amounts of THC and CBD. A strain with balanced ratios may produce a milder experience. Strains dominated by THC can lead to a stronger, more intense high. Understanding the ratio of these compounds can help users choose products that better suit their needs.
Neuroimaging Insights
Brain Scans Reveal Changes
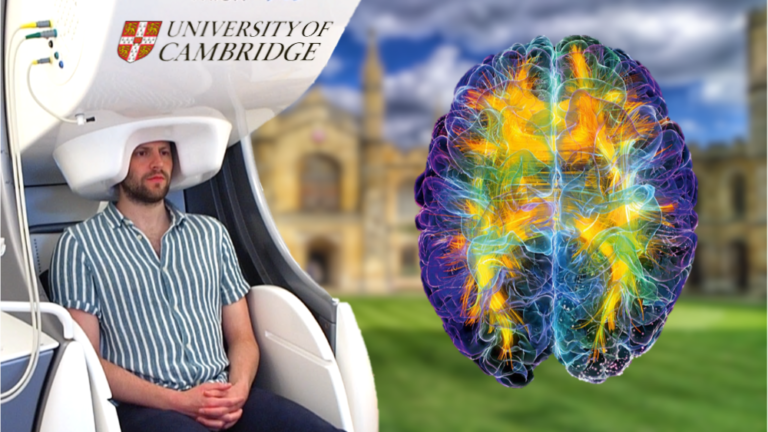
Modern brain-imaging tools, like MRI and fMRI, allow scientists to see how cannabis changes brain activity. These scans can show blood flow patterns, structural differences, and how various brain regions communicate.
Memory and Attention Networks
Some studies have linked heavy cannabis use to reduced activity in memory-related brain regions, like the hippocampus. This might explain why cannabis can impair short-term memory. Other scans show changes in areas that control attention and decision-making, raising questions about long-term effects on mental focus.
Reward Circuits and Motivation
Neuroimaging also highlights changes in the reward circuits of the brain. With repeated cannabis use, these areas may become less responsive to everyday pleasures. This can lead to reduced motivation and an increased craving for the drug itself.
Individual Differences
Not everyone reacts to cannabis in the same way. Genetics, age, and previous experience can influence how the brain responds. Neuroimaging research helps identify these differences, guiding clinicians and policymakers in making informed decisions.
Safety and Medical Potential
Therapeutic Uses
Cannabis-based medicines have made their way into healthcare settings. The NHS, for example, allows the use of CBD-based treatments for certain severe forms of epilepsy, including Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. These conditions are hard to treat with standard medications. Adding CBD as a secondary option can improve seizure control in some patients.
Limits and Regulations
While CBD medications have shown promise, there are important limits. They must be prescribed by specialists and are not suitable for every patient. These treatments may not work for everyone, and some users may experience side effects. Strict monitoring ensures that patients receive the correct dose and treatment plan.
Safety Concerns
Cannabis is not risk-free. Heavy use can harm mental health and might trigger anxiety or psychosis in vulnerable individuals. Driving or operating machinery under the influence is dangerous. There is also a risk of dependence, especially for people who start using young or use it frequently.
Responsible Use and Ongoing Research
Scientists continue to investigate safe ways to harness cannabis compounds. They aim to isolate the helpful properties and limit the harmful ones. This work may one day lead to new medications that offer relief without serious side effects. Until then, caution and awareness are essential.
Conclusion
Cannabis can affect the brain in surprising and complex ways. From altering neurotransmitter levels to reshaping key brain networks, its impact is not always straightforward. THC and CBD influence the brain differently, offering both risks and potential benefits. Neuroimaging studies help us see these changes, guiding better understanding and safer use.
While cannabis-based treatments show promise for certain conditions, their use remains carefully controlled. Knowing the potential dangers can help people make informed choices. By staying aware of new research and following medical guidance, we can move towards a more responsible relationship with cannabis. For a deeper look at these findings, watch my YouTube video! There, I break down the science even further, helping you understand how cannabis may influence your mind and life.
Thanks for reading and please comment on YouTube with any questions! Click here to see the other blogs and associated videos I have about neuroscience! 🙂
If you want to support this evidence based neuro-explainer content then feel free to buy me a coffee or become a patreon! 😊
References
Weed during fMRI: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33592558/
Brain structure changes: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2781289
Psychosis risk increased: https://www.thelancet.com/article/S2215-0366(19)30048-3/fulltext
Anxiety and depression risk increased: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2723657
CBD reduces anxiety: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21307846/
CBD for epilepsy: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30390221/
Pain from multiple sclerosis: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3394820/
Pain from cancer: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28785408/
Post-surgery pain: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14581124/
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Cannabis remains a controlled substance in many places, and its use should be in compliance with local laws and regulations. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before considering any form of treatment.